The objective of the MSAR Government in promoting the development of sport for all is to ‘promote physical exercise among the public and enhance residents’ physical fitness’ using physical fitness tests and evaluation criteria to measure the physique indexes of residents, which are effective means of encouraging and guiding the general public toward carrying out regular physical exercise.
To this end, the Macao Sport Development Board has launched the ‘Physical Fitness Evaluation Program for Participants of Sport for All Gymnastic Classes’ since 2008 at the Tap Seac Multisport Pavilion, with a view to introducing the physical fitness test into the classes. Residents can learn about their physical fitness condition when participating in sports exercises, and have a better understanding of the benefits gained from scientific exercise training and to experience the fun of sport.
This year, the Macao Sport Development Board conducted the program from June to October. The following is the brief report of the program.
1. Number of participants:
A total of 922 participants received the physical fitness test. Among them, 832 participants successfully completed the test, with 80 males and 752 females, the highest number of female participants was found in the age group of 40-59. This reflects the fact that the sport for all Sport for All Recreation and Fitness Class is more popular among middle-aged women.
2. Overall fitness level:
The overall physical fitness condition of the participants of the sport for all gymnastic classes was ideal. According to the ‘Macao residents’ physical fitness standards’ which were set after the Macao Residents Physical Fitness Monitor Work conducted in 2005, 92.2% of the participants reached an overall fitness level of satisfactory or above, indicating an improvement compared with the past two years.
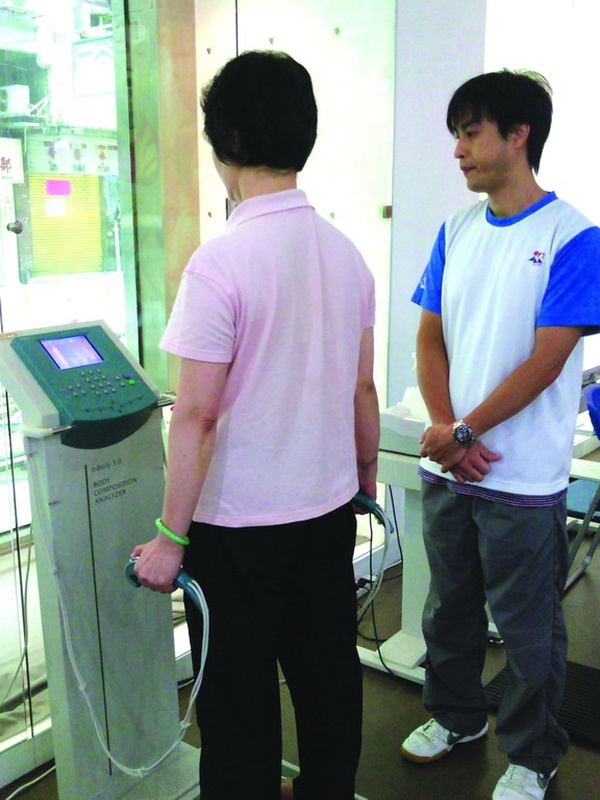
3. Body shape:
The body shape test measures the height, weight and BMI of participants and conducts evaluations based on the BMI index in the ‘Macao residents’ physical fitness standards’. The results show that the percentage of underweight men and women was relatively higher. To increase muscle mass, participants were advised to control their daily intake of calories and participate in weight-bearing exercise such as lifting dumbbells, push-up or using an elastic band to exercise the muscles.
In addition, the percentage of individuals with higher body fat to muscle ratio was also relatively higher. The results show that the participants should focus on reducing their body fat and increasing muscle mass. They are also advised to carry out more aerobic exercise such as swimming, running, cycling and muscle training exercise to achieve the goal. When doing aerobic exercise, it should not be less than 3 times a week and each session should not be less than 30 minutes.
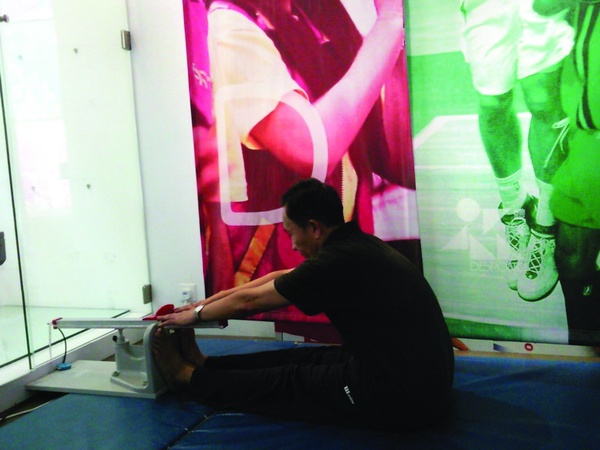
4. Physical function and quality:
The assessment is based on the criteria of a vital capacity and step test index average and the ratio of the number of participants in each group. In terms of physical function, more than 80% of the male participants and over 76% of female participants reached the fitness level of satisfactory in the vital capacity and step test. In terms of physical quality, more than 72% reached the satisfactory level of fitness, indicating a higher level of response and balance abilities. However, the strength of the participants was below average, in particular in the grip strength and standing long jump, with only 46% and 25% reaching the satisfactory level. The percentage of women who have reached the satisfactory level of fitness in the standing long jump was significantly higher than men. In addition, 26% of the participants failed to reach the satisfactory level of fitness standard in flexibility. The results indicate that the participants should increase training in strength and flexibility. To effectively improve physical fitness, participants were advised to enhance their strength with squatting jumps, push-ups or exercise with an elastic band. Meanwhile, stretching exercise can also enhance the body’s flexibility and reduce the risk of muscle strains and injuries.
In addition, regarding the medical history of the participants, there was a certain percentage of participants who suffered from high blood pressure, diabetes or heart disease and other sicknesses, of which the male and female participants respectively accounted for 28.8%, and 33.3%. This indicates that some of the participants of the classes suffered from chronic diseases and they might have been aware of the need to participate in physical exercise in order to improve their health condition. It also reflects that the general public starts to have a higher level of awareness of physical fitness.